
What is the reason solar activity is an 11-year cycle? How does the solar wind occur? What is the structure in which the outermost corona of the sun is heated to more than 1 million degrees? These are some of the sun’s mysteries that also affect the global environment. Solar activity can be described as cosmic weather.
Solar Orbiter, a solar probe jointly developed by the European Space Agency ESA and NASA to solve this mystery, departed from Earth exactly a year ago. As of February 10, 2021, it has already reached the midpoint of the distance between the Earth and the Sun, and is expected to approach 42 million kilometers from the Sun’s surface in the near future.
The Solar Orbiter’s path to the sun is not a straight line, but is drawn in a spiral by the gravity of the sun. It is expected that it will be possible to observe the high-resolution corona appearance that has not been seen before by repeatedly moving around the sun. For this purpose, Solar Orbiter was equipped with up to 10 types of observation equipment on its main body, and already sent images of Venus, Mars, and Earth at the same time.
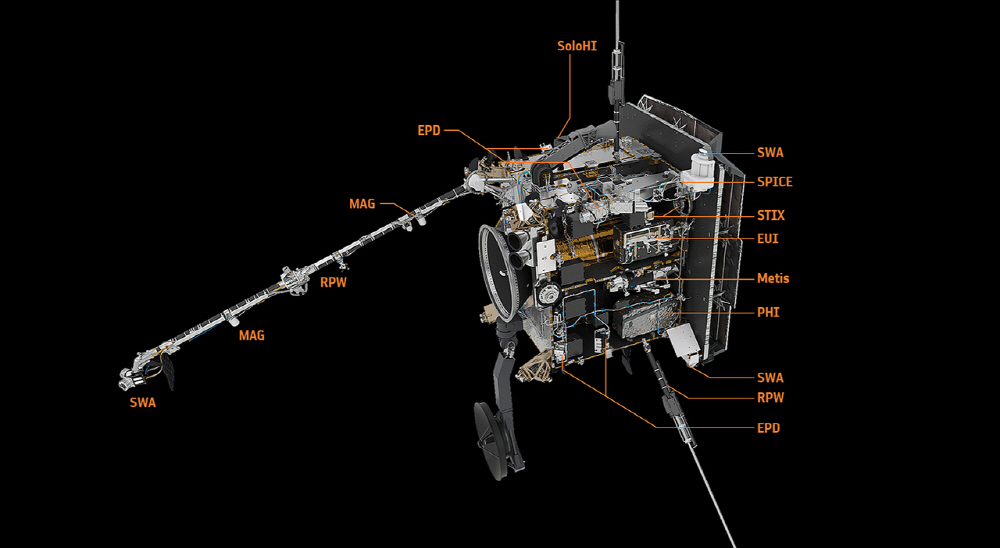
According to ESA, six out of ten devices are specialized in remote sensing technology and are used to observe solar corona. The remaining four are used to increase understanding of the solar wind and solar magnetic field by observing particles flying into the solar orbiter.
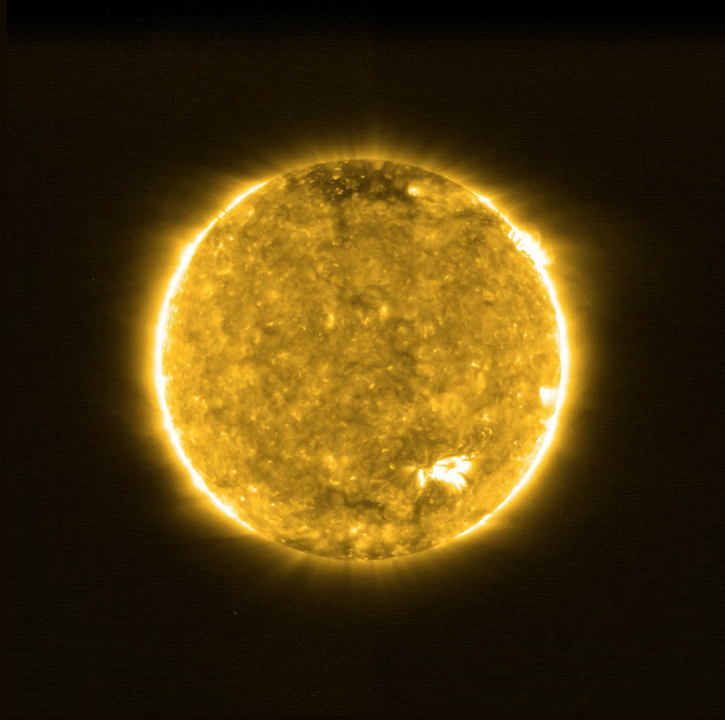
The Solar Orbiter Mission captured the sun through an extreme ultraviolet telescope on May 30, 2020. As a result of analyzing this image, a new flare phenomenon that is hundreds of millions of times smaller than the solar flare observed from the Earth was discovered, and it became known as the solar campfire. In the future, as the Solar Orbiter approaches the sun more, it is expected that the appearance of the sun that has not been seen until now will become more visible.

However, all the data sent by the 10 observation devices mounted on the Solar Orbiter are raw 0 or 1 raw data. How to interpret this is up to the scientist. In order to broaden the scope of interpretation, Solar Orbiter stands for the most open and open mission in science history. The data obtained will be open to the world as well as the team that developed the observation device.
In fact, the raw data sent by Solar Orbiter can be viewed or searched by anyone on the website . The first data were published in September 2020, and in parallel with the data, a number of open-access research papers were also published in the Internet edition of the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics. This allows any national scientist to access and scientifically analyze Solar Orbiter data, and hundreds of scientists around the world are already working together to analyze the data.
Solar Orbiter is also planning to link with Parker Solar Probe to observe the sun. Related information can be found here .


