Israeli semiconductor startup Wiliot has developed a battery-free Bluetooth sensor tag. The battery-less tag already has the electromagnetic induction power generation method such as NFC put into practical use. Willot’s Bluetooth tag also has the same principle. But the thing is that we use electromagnetic waves that are overflowing around us, such as WiFi or Bluetooth smartphone.
This generation of electromagnetic waves is not entirely new. It has been studied in the field of environmental power generation for several years. In 2015, Nikola Labs launched crowdfunding with the iPhone case, which was developed using cell phone waves.
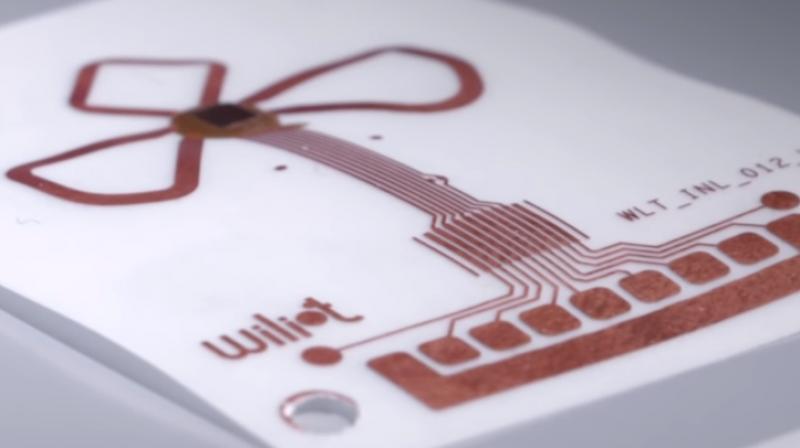
Willot bluetooth sensor tag uses electromagnetic wave power generation and uses paper and plastic printed antenna. It does not need a built-in battery, so it’s just a stamp size, even with an antenna. You can also use Bluetooth to send static IDs, as well as connect weight and temperature sensors to send the information.
Batteryless Bluetooth tags can be used for a variety of purposes. For example, if you use the tag to prevent loss, you do not have to worry about the battery in case of emergency, and you can use it for warehouse management in warehouse or shop. However, there is no information about how much electric power can be actually obtained through electromagnetic wave generation and how the intensity of the Bluetooth signal becomes. At least the demo video can communicate at 3m distance.
The product will begin shipping sampling this year and will be available from the second half of 2020. Willot has also attracted $ 30 million in funding from investors such as Amazon and Samsung Electronics. If a company can commercialize it with technology that attracts attention from large corporations, it is possible that it will spread quickly. For more information, please click here .


