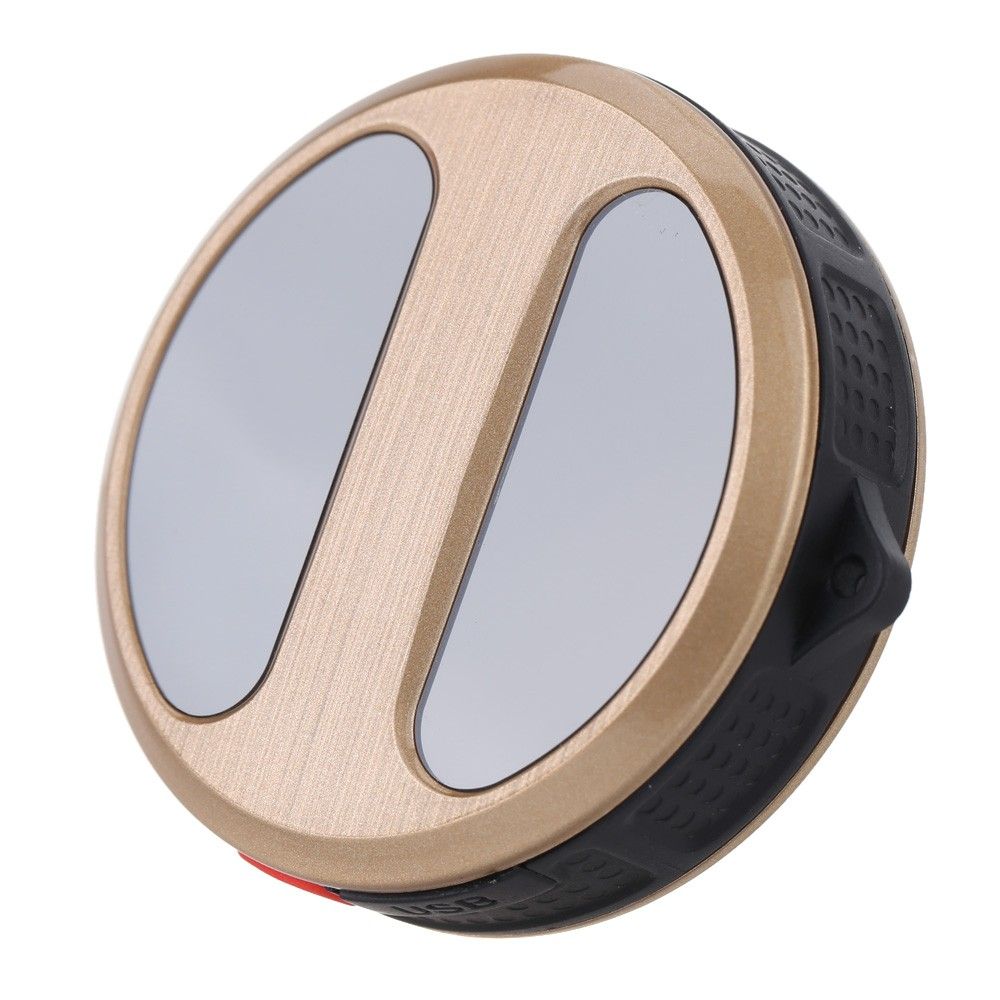

A GPS tracker that can specify a location such as a smartphone using GPS is a device used to locate children, pets, and cars. The inexpensive one is about 20,000 won and can be purchased on Amazon. However, according to security company Avest Software, 600,000 GPS trackers are vulnerable to eavesdropping and spoofing attacks.
The GPS tracker transmits the location information acquired from the GPS module to the communication module and enables the owner’s location to be captured. The GPS tracker itself is simple and inexpensive, but some can use the phone function by pressing the SOS button or play sound through the built-in speaker. The location information sent by the GPS tracker can be uploaded to the cloud and viewed through a web app or a smartphone app.
According to Avast Threat Labs, a Chinese-made T8 mini was purchased to analyze the processing process, cloud-to-cloud traffic app and cloud-to-cloud traffic on a GPS tracker. This product is a key ring-sized GPS tracker and is a model that enables two-way communication with SOS button, speaker, and microphone.
When you log in to the web app, you can view location information. On Google Maps, GPS tracker location and manufacturing identification number, online status, battery level, location information acquisition date and time, and stop time are displayed. However, the web app version login form can be viewed as HTTP protocol rather than HTTPS protocol, which is an encrypted communication. The manual says that the default login ID and the default password for the GPS tracker manufacturing identification number are set to 123456. Surprisingly, it says that in order to register a user name in the user ID, you need to contact the retail store where you purchased it. Explain that what is set with the manufacturing identification number and 123456 password is obviously accessible from the retail store.
In other words, user account information is transmitted over the Internet without being encrypted. He pointed out that if the default password is not changed, there is a possibility that a malicious attacker can easily hijack the GPS tracker. Due to this vulnerability, an attacker can easily check the location information of the GPS tracker, and remotely use the SOS function to activate the two-way communication function and eavesdrop on the attacker’s device.
Avast also analyzed the manufacturing identification number of the GPS tracker. According to this, the manufacturing identification number displayed on the web app is an 11-digit number. It means that it does not conform to the standard requiring 15 digits. As a result of continuing investigations by AVEST, it was found that the only thing displayed was not the real manufacturing identification number, but the only ID created based on it.
Avast searched 1 million IDs with the first 4 digits of 1703 and found that 600,000 of these devices were running with the default password of 123456. At least 167,000 are said to have been able to search for location information online. In addition, because the same system or API is used, this problem was confirmed not only on the T8 mini, but also on 30 different GPS trackers. About this problem, Avast notified the GPS tracker company in June, but there was no reply from any company until September. Related information can be found here .

