
The Telecom Operators Association GSMA has released its annual report on the status and prospects of mobile business. According to this, 5G, the next-generation mobile communication standard, has actually started to be used in 24 markets around the world.
5G is an advanced network technology that is up to 100 times faster than LTE currently in use. The latency is reduced by a few milliseconds and more devices can be connected. The introduction of 5G is expected to bring about a new wave of smart services that not only strengthen the use of real-time AI, but also promote the digitization of various legacy businesses.
In last year’s report, the GSMA did not give a clear number of markets for 5G. He pointed out that 5G technology is becoming a solid reality, citing the fact that 5G began in the US and Korea at the end of 2018. It is also predicted that 16 major countries will start 5G by the end of 2019. This year’s report highlights the great market traction of 5G. On January 20, 2020, 79 operators from 39 countries announced plans to launch commercial 5G services.
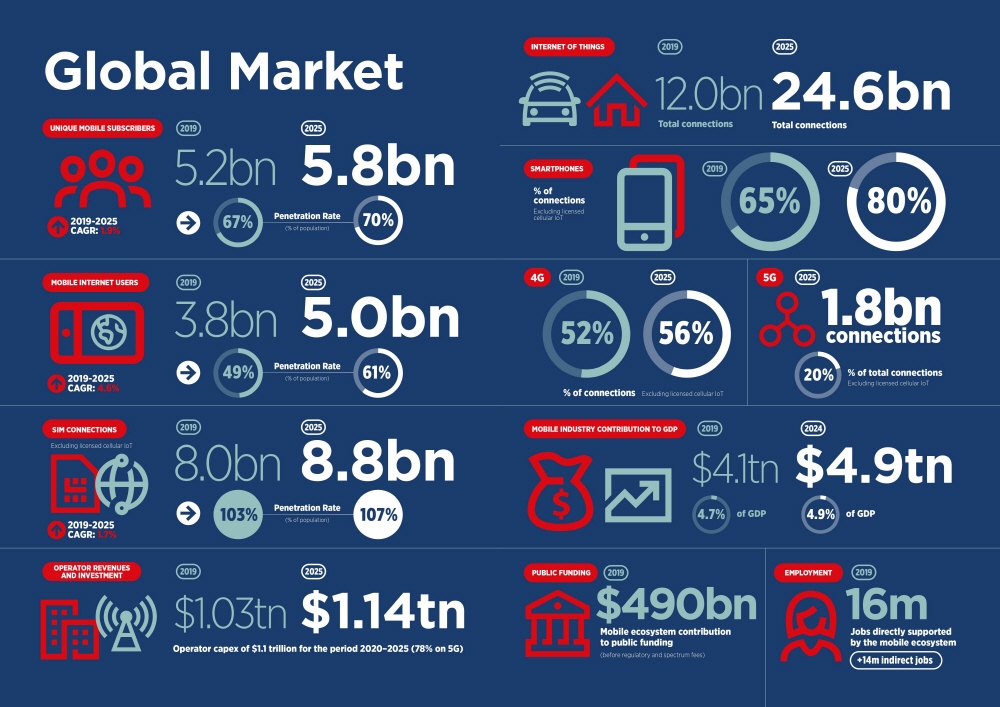
Compared to 4G or the previous generation, the 5G share will be a fraction of the time. According to the report, 4G will be the dominant mobile technology in 2019. The number of sessions is over 4 billion, accounting for 52% of the total number of sessions. The GSMA predicts that 4G will continue to grow over the next few years, reaching a peak accounting for less than 60% of global sessions in 2023. 5G is predicted to be 20% of global sessions by 2025. It is expected that active development is expected in advanced Asian regions, North America and Europe.
Expanding Xingya, nearly half of the world’s population, or 3.8 billion, is mobile Internet users from 2G to 5G, and by 2025 this number is expected to increase to 61% or 5 billion. However, it needs to be emphasized that 5G is not introduced as a universal service. In fact, 5G tends to target the center of the city. The 24 markets that introduced 5G services also have a fairly low coverage rate compared to the population.
But most importantly, consumer demand for next-generation device connectivity has not yet occurred. Although the GSMA report is a life and death for mobile operators, it separately investigated whether consumers would be willing to pay for 5G. In markets such as the UK, Australia, Spain, and Italy, adults are less motivated by the high price of 5G technology awareness. Less than 35% of respondents said they would like to upgrade to 5G. Likewise in the US market, 5G popularity is high, but the demand for upgrades is a little over 40%, a little higher than in Europe.
The GSMA points out that mobile operators should work harder to increase data rates as well as increase awareness of other benefits. This requires 5G marketing to appeal to the expansion of mobile provision regions, innovative new services, and the connection of various IoT devices that are not already connected.
Of course, this report makes it clear that there are differences in the degree of IoT devices outside of China, but the demand is not high. Nevertheless, the GSMA predicts that billions of IoT devices will be connected over the next five years. From 2019 to 2025, the number of IoT device connections worldwide is expected to grow to 25 billion, more than doubled and tripled to $1.1 trillion.
The GSMA also said that one of GAFA (Google, Apple, Facebook, Amazon) will be split during the forecast for 2025. While this bold prediction didn’t point to a specific company, most Americans are paying attention to Google. The GSMA said that in the short term, at least one AR glass from a leading manufacturer will enter the market in large quantities, and pointed out that health-related wearable devices will be part of a solution to reduce the load on the public health system.
It is predicted that 5G in 2025 will be the first technology in the mobile history that has a greater impact on businesses than consumers. It can be said to be an euphemistic explanation of the background of low consumer demand for 5G. Consumers are less willing to pay more than now in exchange for speed improvement, and mobile operators are expecting corporate demand.
The report stated that government regulations should play a role in promoting the commercial use of 5G and implementing incentive policies promoted by all sectors of the economy. Related information can be found here .

