Under the Artemis plan to send humans back to the moon, NASA has developed the LunaNet architecture to scale activity on the moon.
Communication with the ground in space missions relies on pre-established connections such as space relays and ground antennas. The problem with this approach is that communication opportunities and efficiency can be limited when running multiple missions in parallel. Lunanet provides Internet-like network access, allowing users to stay connected to large networks and eliminate the need to pre-book data transfers.
The Lunanet core network framework ensures that data flows smoothly through the network and reaches its final destination, even if the signal may be disrupted in the delay-tolerant network DTN. When two Lunanet nodes fail, the node stores data until the path is restored.
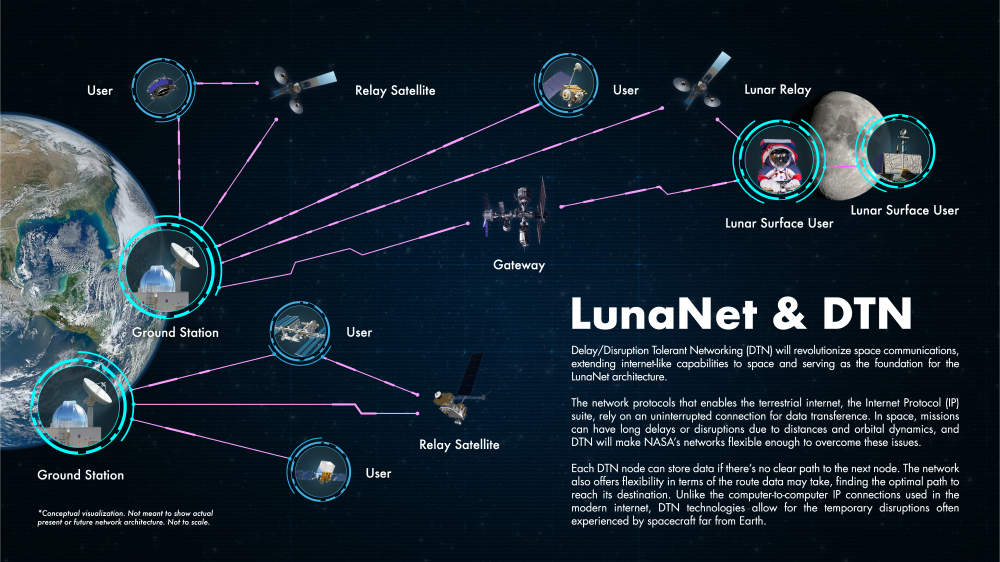
In addition, Lunanet maintains high precision in lunar navigation and secures operational independence in processing data on Earth. Missions using Lunanet navigation can get everything they need for autonomous lunar flight, regardless of orbit, with access to key measurements needed for orbit determination and guidance system operational positioning.
According to NASA, Lunanet provides a new Earth-agnostic navigation paradigm and can quickly locate itself in manned robot missions and provide feedback to planned systems.
In addition, Lunanet’s detection intelligence service provides users with alerts and other important information, greatly improving the situational awareness of astronauts, rovers and other assets on the moon. For example, when space weather equipment detects hazardous solar activity, it can alert users directly, rather than waiting for instructions from network administrators on Earth.
NASA said that the safety and health of astronauts is an important concern in the Artemis program, and that it is preparing for unforeseen events by using the Lunanet search service to provide location data to NASA’s distress signals.

Lunanet Science Services also provides measurement opportunities for researchers on Earth using radio or infrared optical communication links. A network of nodes provides an opportunity to observe the lunar baseline and enables frequent measurements for long-term comprehensive study of the lunar environment. The nodes can also be deployed to enable lunar regional or global-scale observations and give scientists access to lunar data at large spatial scales.
Lunanet antennas have the potential to be used for applications such as radio astronomy by finding radio radiation from distant celestial bodies. These capabilities provide scientists with a platform to validate new theories about space science and deepen their scientific knowledge. Related information can be found here.




















Add comment