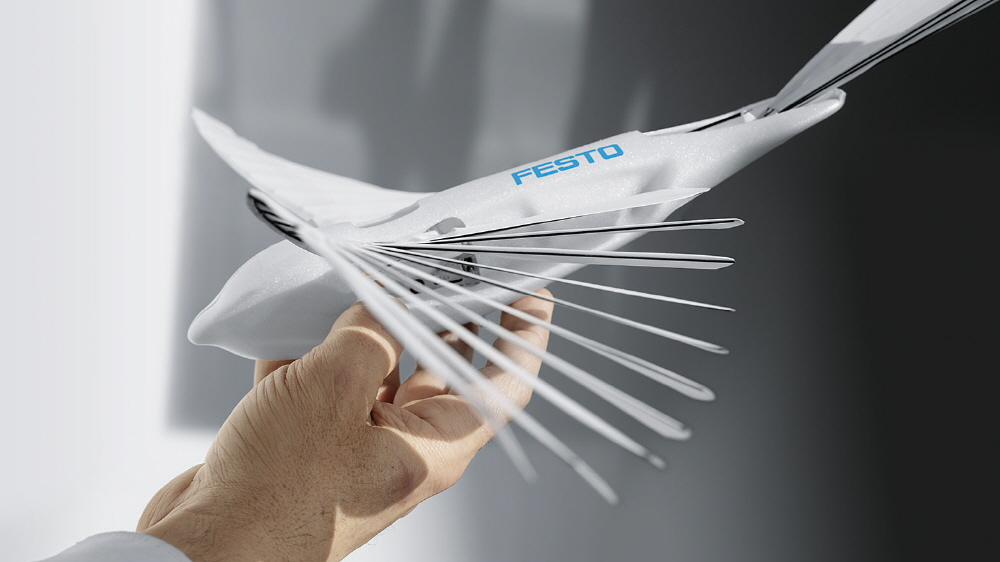

BionicSwift is a new form of autonomously flying robot from Festo, a German-based company. It flaps its wings like a real bird, and when viewed from a distance, it may be mistaken for a bird.
Pesto designed the robot based on the algae’s biological characteristics and ultra-lightweight structure. The body length of Bionics Wift is 44.5cm, the width of the wing is 68cm, and the weight is only 42g. The company is explaining the reason for adopting the ultra-lightweight structure by saying that the lighter weight of the robot means less material and energy consumption.
The body is pure white, with a simple design consisting of two wings and tail feathers. Wings and tail feathers move up and down. Festo explains that Bionicswift is modeled on bird feathers to make flight control as faithful as possible. The materials that make up the wings are lightweight and flexible, but they are solid and overlapping. When this robot reproduces the movement of its wings, each time the wings move upward, the individual plates are recreating a mechanism that allows air to flow from the wings to restrain the force required for the bird to move the wings. Conversely, moving the wing down consumes a lot of power to close the plate, but it can create a lot of lift.
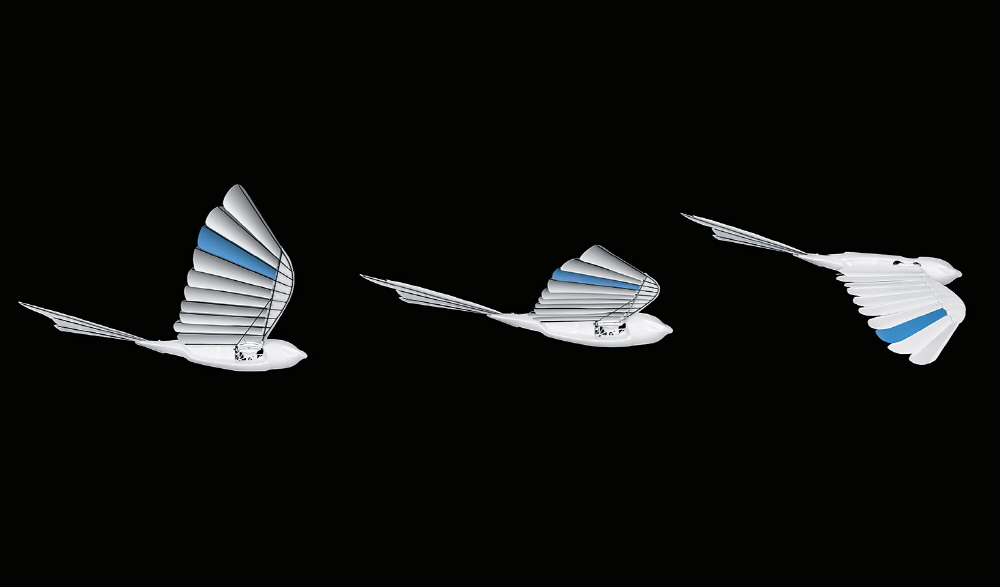
Bionics Wift is equipped with a wing device and communication system, components necessary for wing beat control, a brushless motor, two servo motors, a battery, a gearbox, and a circuit board. It prevents the wing from moving and can glide or fly like fallen leaves and change the direction of travel.
In addition, it is possible to fly in formation with several units using a wireless module that supports UWB ultra-wideband wireless communication. In formation, multiple radio modules must be installed instead of anchors in the space flying Bionicswift. This makes it possible for Bionics Wift to receive the signal from the wireless module and accurately determine where it is flying indoors. Also, the actual control of the flight is that the flight path can be programmed on the master computer, which organizes and processes the information collected by Bionics.
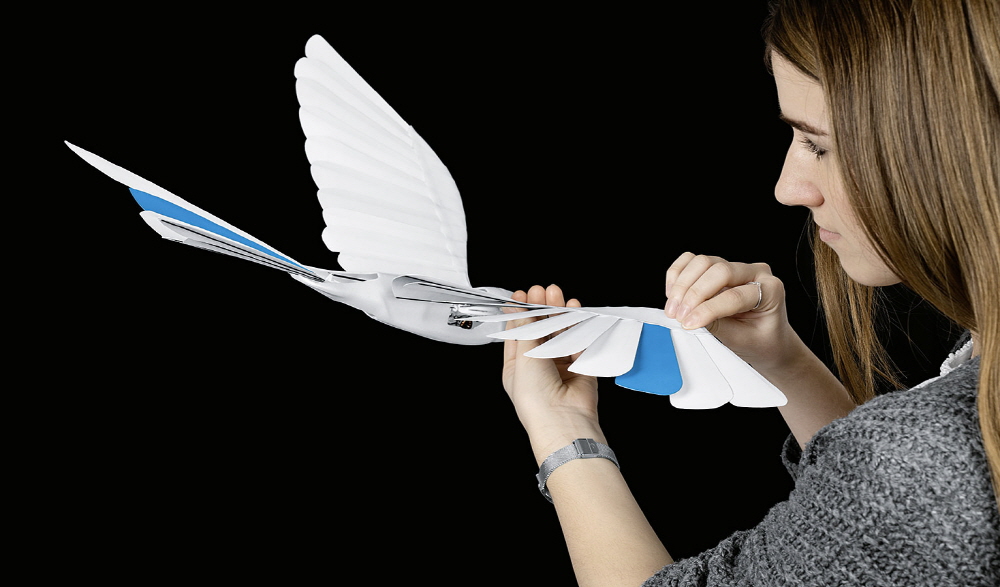

Bionics Wift can autonomously fly back to its path if it leaves the flight path due to external environmental influences such as wind and heat. It is explained that even if it is in a place where physical contact is not possible for wireless communication, it can detect the exact location so that it can fly safely and without problems.
Festo says that it is possible to realize advanced 3D navigation systems in networked factories in the future with autonomous flying robots such as Bionics Wift and routing technology using wireless communication. In addition, it is explained that it is possible to use a system that accurately grasps the flow of materials and products, transports materials using an autonomous flying robot, or optimizes flight paths. Related information can be found here .


















Add comment