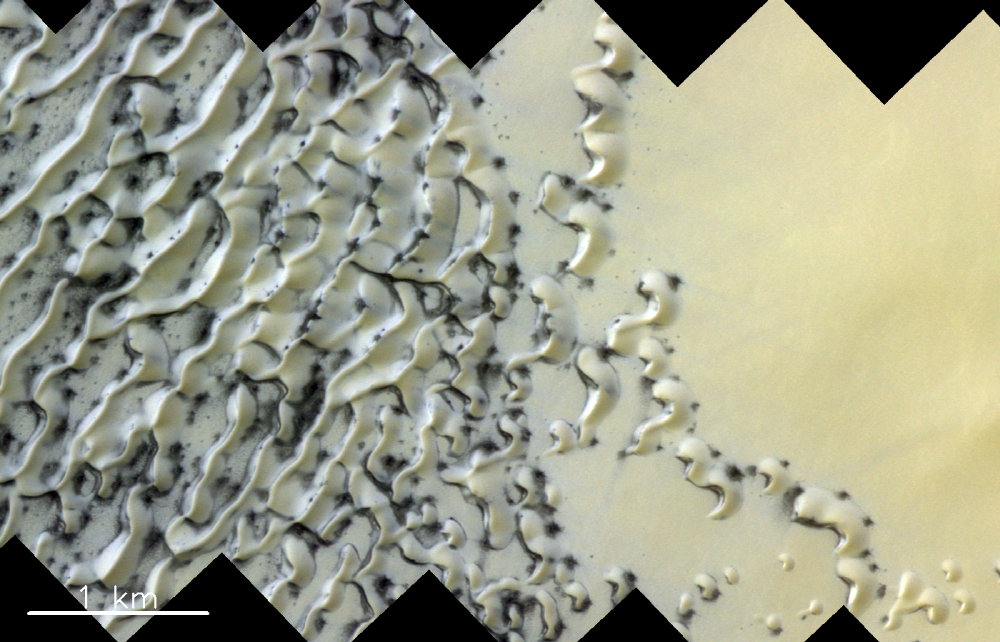
This is the image captured by the European Space Agency’s ESA with the multi-color stereo surface imaging system CaSSIS mounted on the TGO of Los Cosmos and the probe ExoMars. The image of a hill covered in ice is it. The black speckled identity in the image is the sand that the gas erupted from ice spewed on the surface.
Martian dunes are formed by sediments moving in the wind like Earth. According to the ESA, scientists can observe the location of the dunes to get wind clues. This image shows how frozen carbon dioxide sublimates and spews blackish sand when the gas erupts onto an ice-covered surface.
Mars’ polar region is already being studied. It is believed that a large amount of water, including liquid, exists. But the TGO is also asking for information on the planet’s gases, such as methane. Studies so far have found that Mars methane concentrations change from season to season and rise this year. The team wants to understand how active this planet is from a geographic and biological point of view. Related information can be found here .

















Add comment