
It has been reported that January, May, and September of this year had the highest temperatures ever observed every month. In this way, the effects of global warming have surfaced. When talking about such global warming, carbon dioxide is noted, but renowned climatologists such as the Australian Federal Academy of Sciences published a joint study that nitrous oxide, which has a greenhouse effect that is 300 times stronger than carbon dioxide, threatens the future of the planet.
When nitrous oxide is released into the Earth’s atmosphere, it is decomposed by ultraviolet rays to produce nitrogen monoxide, which destroys the ozone layer. In addition, the greenhouse is 300 times larger than carbon dioxide, but it has a short residence period of 116 years compared to the carbon dioxide that remains in the atmosphere for thousands of years, but the concentration in the atmosphere is low. have.
A joint research team with 70 meteorologists from 44 institutions around the world conducted a survey of the total amount of nitrous oxide by humans and found that nitrous oxide emissions have increased by 30% over the past 40 years. The change in the concentration of nitrous oxide in the air is an estimate from the gas trapped during the Antarctic ice cap because no record existed before 1980. As a result, the concentration, which had not changed significantly from AD 200, suddenly increased from the mid-1800s. As of 2018, the concentration of nitrous oxide increased by 22% from around 1750.
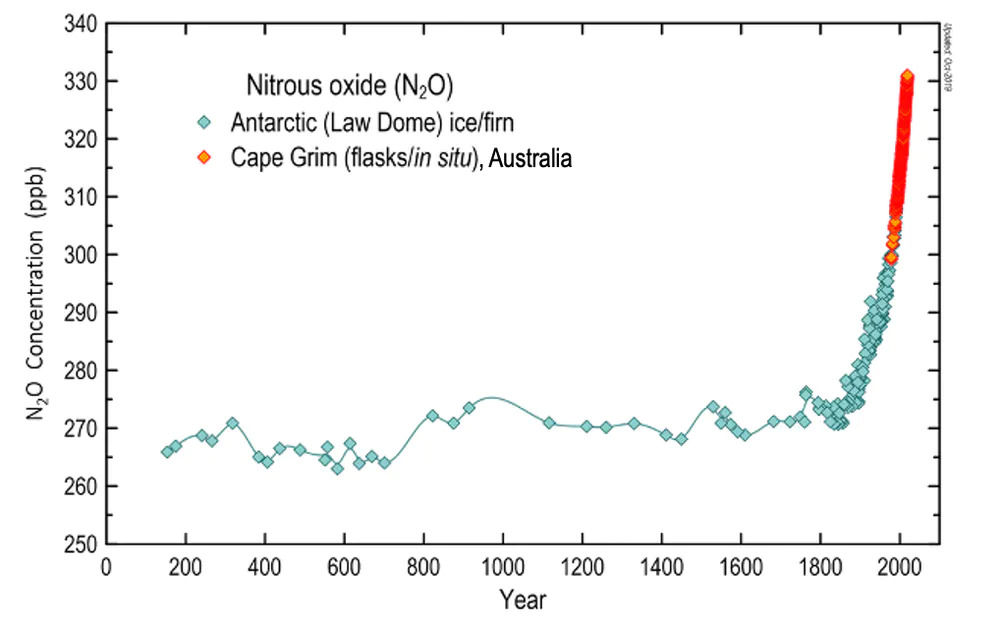
According to the joint research team’s survey, the amount of nitrous oxide naturally released from the soil and the ocean remained almost unchanged. The joint research team cited agriculture and livestock as the main reasons for the rapid increase in nitrous oxide concentration. Agricultural nitrogen fertilizer use and livestock compost production have led to a sharp increase in nitrous oxide, and various human activities, such as chemical industry and wastewater fossil fuel burning, are also related to the increase in nitrous oxide concentration.
The research team is also requesting the rate of change in nitrous oxide concentration by region. According to the survey, countries with rapid economic growth, such as Brazil, China, and India, show a remarkable increase in nitrous oxide emissions as crop production and livestock numbers are rapidly increasing.
A joint research team on nitrous oxide concentrations, which continued to rise, point out that there is a problem that there is no regulation. Through the Montreal Protocol, which regulates substances that may destroy the ozone layer, it is used as a dry cleaning solvent or refrigerant such as chlorofluorocarbon, halon, and hydrochlorofluorocarbon used for cleaning air conditioners and refrigerators and electronic parts. Carbon tetrachloride and the like were regulated. However, there was no regulation on nitrous oxide. In the Paris Agreement, carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide reduction targets were set, but since these were only targets, there was no binding force.
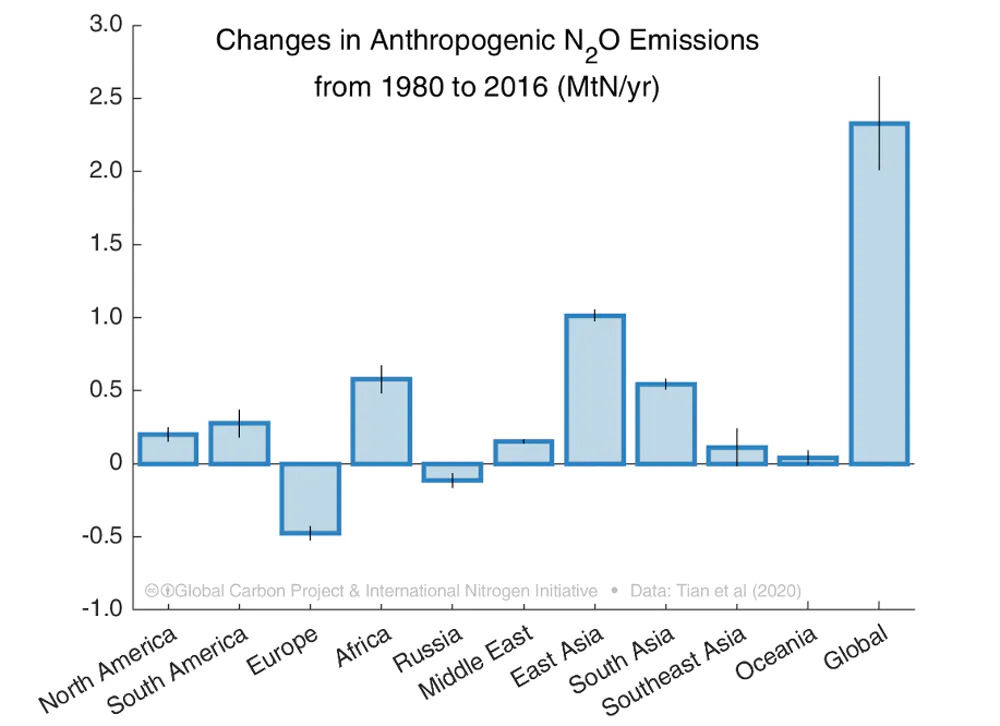
The research team argues that the current concentration of nitrous oxide is increasing at a rate that exceeds expectations, and that nitrous oxide should also be paid attention when discussing efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. A specific method is to strengthen the management of agriculture, livestock and livestock compost, which is a major factor in which the nitrous oxide concentration increases. It proposes methods such as the use of fertilizers optimized for plants and the use of fertilizers with low nitrous oxide emissions to rotate crops that improve soil such as legumes to reduce fertilizer use.
When looking at the quantified annual figures of nitrous oxide in the world, the research team found that the amount of nitrous oxide emitted by human activities is about 7.3 million tons per year. Among them, agriculture accounts for a high proportion of 3.8 million tons. Meanwhile, nitrous oxide emitted by nature is about 9.7 million tons per year, and 13.5 million tons of nitrous oxide is destroyed by chemical reactions in the atmosphere. The increase in nitrous oxide present in the atmosphere by human activity is visually indicated.
The research team revealed that even with appropriate agricultural policies, synthetic fertilizers and compost are currently essential, requiring new technologies such as zeroing actual emissions of greenhouse gases. Related information can be found here .


















Add comment