
NASA’s InSight probe collects Mars weather data and checks the weather on a daily basis to measure Mars’s geothermal and earthquakes. The weather starts in early February and tells you about temperature, wind speed, and pressure. You can see it graphically through the site. Mars is almost inversely proportional to temperature and pressure, and wind speed and pressure are similar.
Insight is experiencing a winter when landing near the Mars Equator and the storms are becoming more active. Observing weather data in harsh environments. The probe can not find traces of storms near the equator at 60 degrees north latitude, but the weather on Mars is already known through pressure, signal traces, and so on. The signal waveforms are characteristic enough to be seen near the equator.
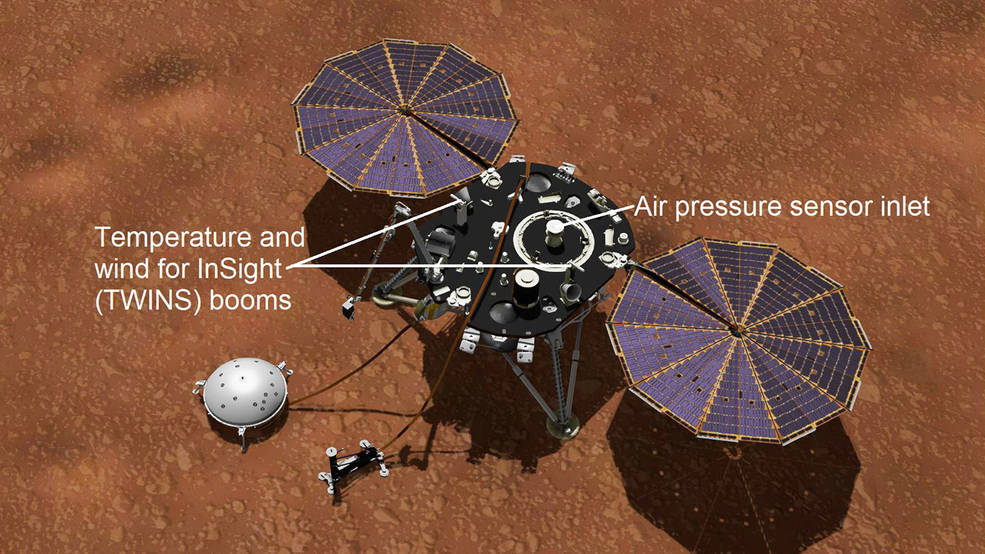
Insight is equipped with sensors developed by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Cornell University and the Spanish Institute of Space Biology to collect this information. This equipment is called APSS and collects data per second during the day of Mars. Of course, the day of Mars is called the SOL unit and it is 24 hours 39 minutes 35.244 seconds.
Because Insight sends the data daily to the district, daily weather forecasts are available. Over the next two years, Insight will be updated daily as much as it continues to collect data.
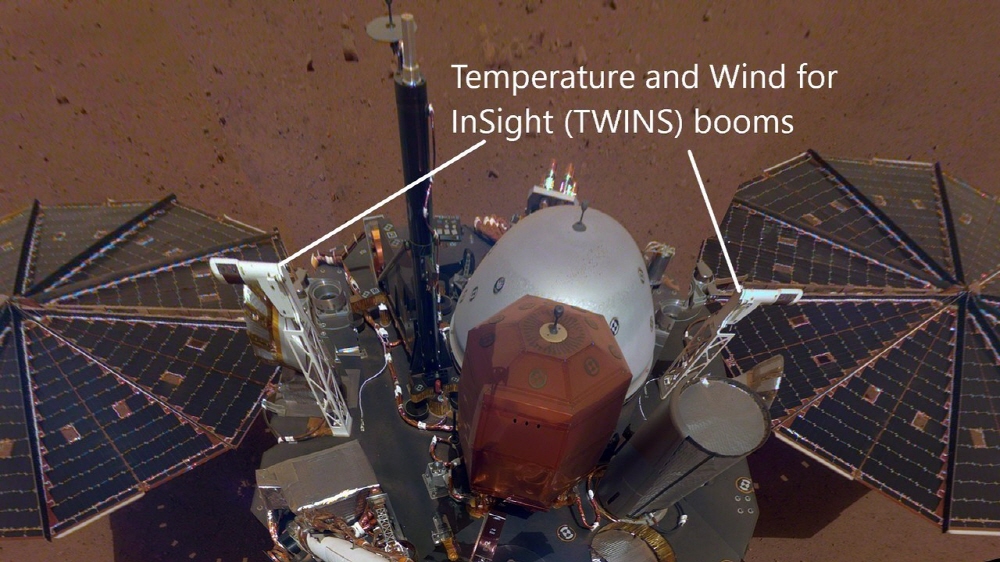
Insight has internal pressure sensors, temperature and wind sensors on the deck, and magnetic sensors on the edge. The sensors are on one side to the east and the other to the west. It tells the research team whether strong winds are interfering with the seismometer.
The researchers say the APSS will eliminate earthquake data and environmental noise signals and let you know when an earthquake has occurred, and will continue to run it to learn more about weather data on the ground. You can also measure the wind and study how sand dust is spilling from the ground. I still do not know how much wind I need to dust in the thin air of Mars. Sand storms, and other factors that affect the impact of sandstorms.
It can also help you to know the dust vortex that left a layer on the surface of Mars. Since the dust swirls are low pressure winds, Insight’s air pressure sensors can detect it in the neighborhood. You can investigate dust vortices that are 10 times more accurate than the vikings fired in the 70s or the 90s massepfinder, and that can be seen a few tens of meters ahead. At the present landed plains, a dust swirl occurs frequently, and the vortex that occurs at low pressure is said to rotate at 100 km / h.
On the planet, the dust swirls of the desert can range from 15m to 1km in height. But on Mars, it is 5 to 10km high. Larger diameter may be 100m or more. Mars weather is here , the relevant information here can be found at.


















Add comment