Robots and AI are evolving and are increasingly replacing jobs that have been done by humans. However, data centers are not changing that rapidly.
Examples of robot introduction include Patchy McPatchbot, Sir Patchalot, and Margaret Patcher used by DE-CIX, a German Internet exchange company. All are patch robots that can handle port provisioning and upgrades in minutes.
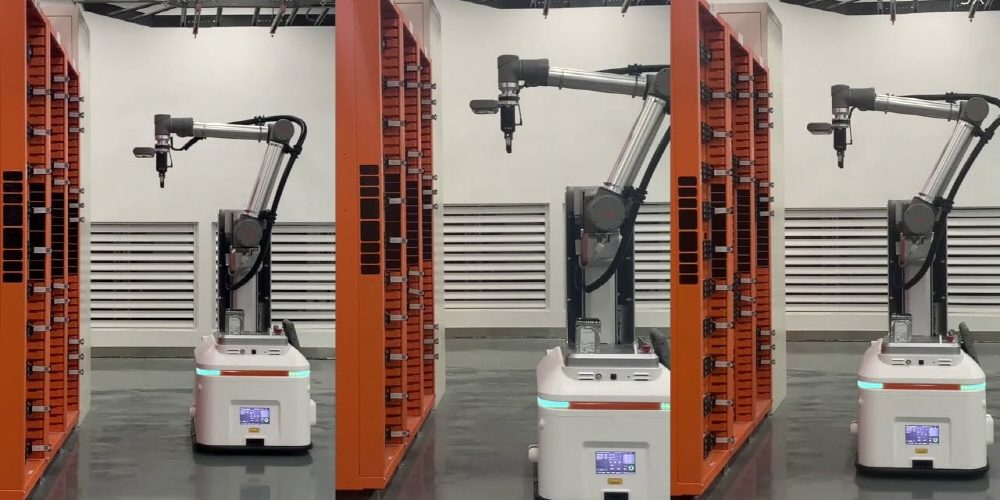
In addition, Alibaba’s data center is introducing a robot that can exchange a broken hard disk without the need for a human hand. The robot can seamlessly handle the replacement process, including automatic inspection, detection of defective disks, and replacement and replacement of disks.
Facebook is also found to be designing robotic solutions for automating and scaling data center infrastructure operations, while Google is also considering deploying advanced robotics systems in its data center.
However, large companies such as Google and Facebook are lagging behind because there are various barriers to introducing robots. Joe Kava, Google’s vice president of data centers, said hyperscale data centers are like warehouses, and that most processes require robots to move to specific locations to perform tasks. Point out that it is much more complicated.
One of the problems is that we try to use randomness to bridge the gap between simulation and reality, but there are gaps that don’t fit. However, in the future, data center design may be fundamentally re-examined to presuppose the use of robots and not consider humans. It is necessary to develop carefully so that accidents do not occur or the server is damaged when human beings are involved.
One expert says that by throwing away some of the anxiety and uncertainty and adopting autonomous intelligent systems, we may be able to solve the challenges we may face in the near future. Related information can be found here.


















Add comment