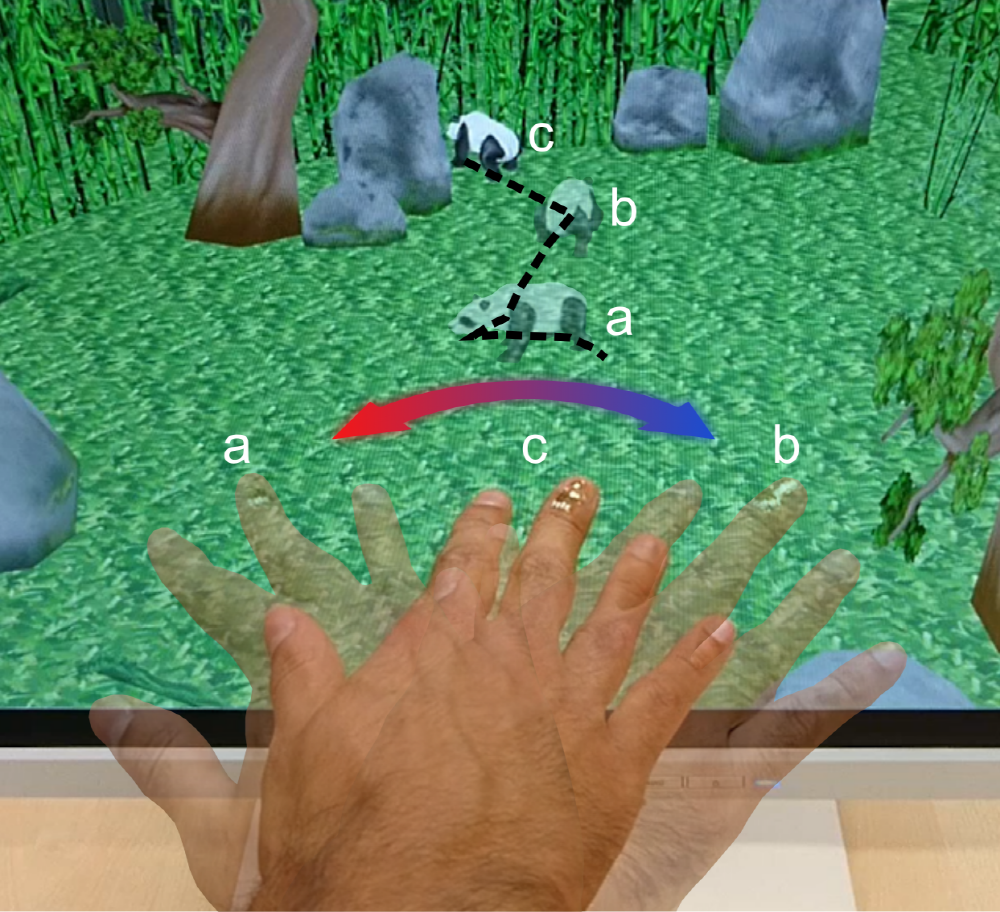
Research team Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) in Germany is studying wearable devices that digitize the Earth’s magnetic field. It is a polymer foil with a thickness of 1/1000 mm attached to the skin called e-skin (e-skin).
The foil is equipped with a magnetic field sensor. It is said to be able to detect a magnetic field of 40 to 60 micro tesla which is 1,000 times weaker than the magnetic field attached to the refrigerator. According to the principle of anisotropic magnetoresistance, when the operating sensor points to the north, the voltage is strongest, and when it points to the south, it is weakest. Of course, you can replace it with a compass, but you can also manipulate content created with game engines with a foil-attached finger. It is to move the direction freely according to the finger movement.
The digit moves to a preprogrammed form to give a digitized voltage signal as the finger indicates north-south. It allows you to manipulate the game with geomagnetism rather than a sensor such as a gyroscope.
This technology can be applied to interactive digital fields such as games. The researchers hope that they will be able to verify the human susceptibility. For more information, please click here .

















Add comment