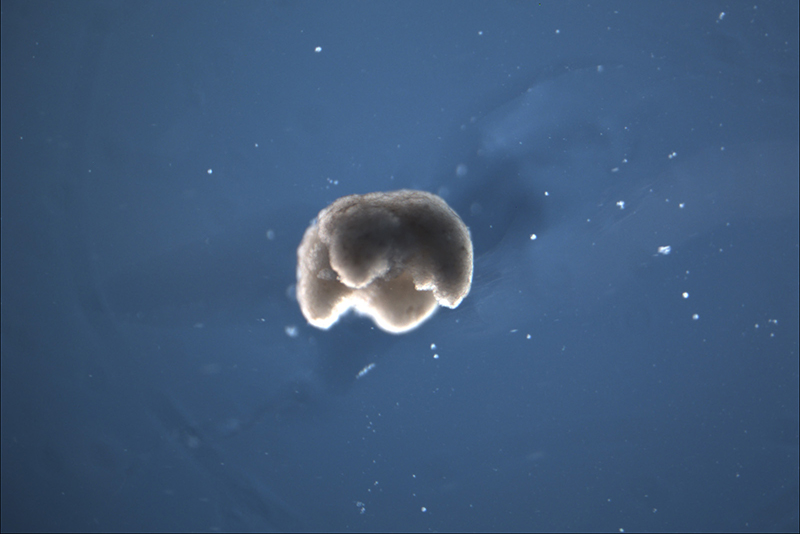
Xenobot is a living robot reconstructed from frog embryo cells. Genobots, which can carry substances while walking autonomously, are expected to prevent arteriosclerosis by carrying drugs to affected areas of the human body or removing waste products accumulated in blood vessels.
It is a research group including Josh Bongard, a researcher on evolutionary robotics at the University of Vermont, who successfully developed this living robot, and Michael Levin, a biologist at Tufts University. The research team first conducted a simulation based on its own evolutionary algorithm using a supercomputer at the University of Vermont. It is said that it has selected from thousands of design candidates to determine what shape and structure living skin cells and cardiomyocytes can be assembled into for efficient exercise.
Next, the research team collected and cultured stem cells from live embryos of the African nail frog (Xenopus laevis). Then, using small-sized tweezers and electrodes, the cells were molded and designed to produce a robot. The name genobot is derived from the scientific name of the African nail frog.
To make a genobot, the stem cells must first be isolated and cultured by opening an African nail frog embryo. Then, the stem cells are molded into a shape designed using a supercomputer. The robot is less than 1mm in size, and the energy required for the activity is stored in the cell, so it can continue to run in water for days or weeks.
Genobots are made of living cells, so they can regenerate themselves even if they are damaged. In addition, because it can be assembled in a free form, it can be stored and transported. In addition, it is being reviewed for purposes such as purifying the sea, removing waste products accumulated in arteries, and discovering radioactive materials.
The research team said that many robots are made of metal, concrete, plastic, etc., but there are many harmful substances in them that adversely affect the human body or the environment. However, they say that if a robot is made from living cells, it will biodegrade after its activity. Gusing emphasizes that the load on the human body or environment is low. In addition, he is planning to develop a genobot equipped with sensory organs such as blood vessels, nervous system, and primitive eyes, and is expected to be able to make a genobot that can be active not only underwater but also on land if it is produced with mammalian cells.
On the other hand, one expert expressed the view that the ethical problem is inevitable, saying that the Xenobot research will face a difficult problem as to whether living robots are living things or machines. The research team is not only aiming to develop more advanced genobots in the future, but is also planning to improve understanding of birth defects and age-related diseases by analyzing the biological processes by analyzing the genobots with new biological structures. Related information can be found here .


















Add comment